
If you need to change the order of some bootloaders, you can use the “-o” option. You can use the “-v” option with efibootmgr to see if everything is alright. The grub圆4.efi is registered in the firmware settings, so we can boot it. This is something we can work around with rEFInd.Īt this point we have the file EFI/GRUB/grub圆4.efi and the /boot/grub tree. Then we should either put an entry manually in grub.cfg. So it will not be able to generate an entry for it in the grub.cfg. One interesting thing here is that, in case Windows is installed, grub-mkconfig says it detects the Windows bootloader (bootmgfw.efi) but does not support it. # grub-install -target=x86_64-efi -efi-directory=/boot/efi -bootloader-id=GRUB -recheck -debug → Then we install the GRUB bootloader on the EFI partition.
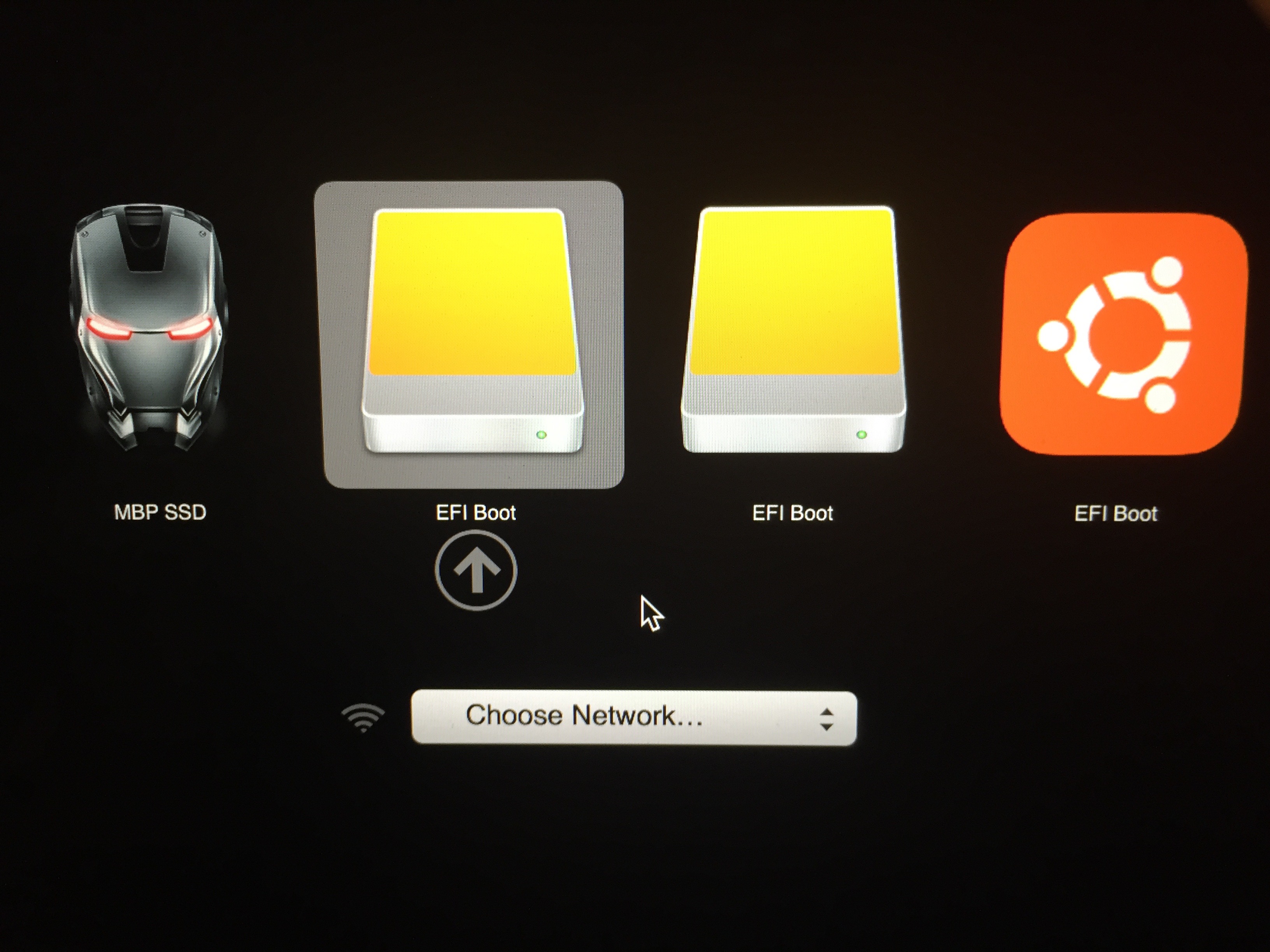
# chroot /mnt env -i HOME=/root TERM=$TERM ' PATH=/usr/bin:/usr/sbin:/bin:/sbin bash -login +h → Mount some useful filesystems (if they are not already present): Use the df command to see what else is mounted and where. Normally the newly installed system is mounted at /mnt. We will chroot into our newly installed system right away. So, just after the installation process, do not reboot.
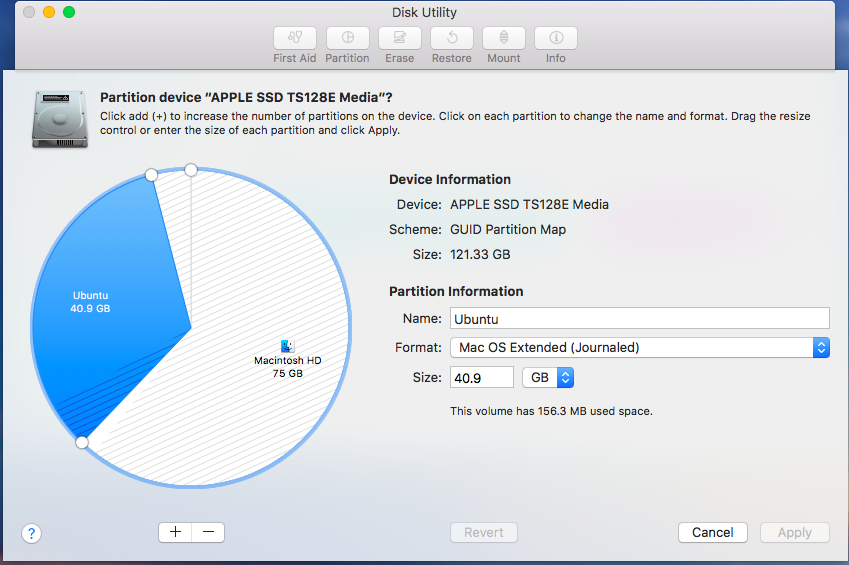
If ELILO was not installed then we need to initialize GRUB in order to have a bootable system.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
